Hair Growth FAQs
Here are the most common questions about hair growth, based on medical insight and real patient concerns. This section helps clarify expectations, timelines, and factors that influence results.
How fast does hair grow per month?
On average, hair grows about 1 to 1.5 centimeters per month. Growth speed varies based on genetics, age, health, and scalp condition.
Can diet really affect hair growth?
Yes. Hair follicles rely on nutrients like protein, iron, and vitamins. Deficiencies often lead to thinning and increased shedding.
Do hair supplements work?
They can help if you have deficiencies. Without deficiencies, their effect is usually limited.
Is it normal to lose hair every day?
Yes. Losing up to 100 hairs per day is normal. Ongoing excessive shedding may signal an underlying issue.
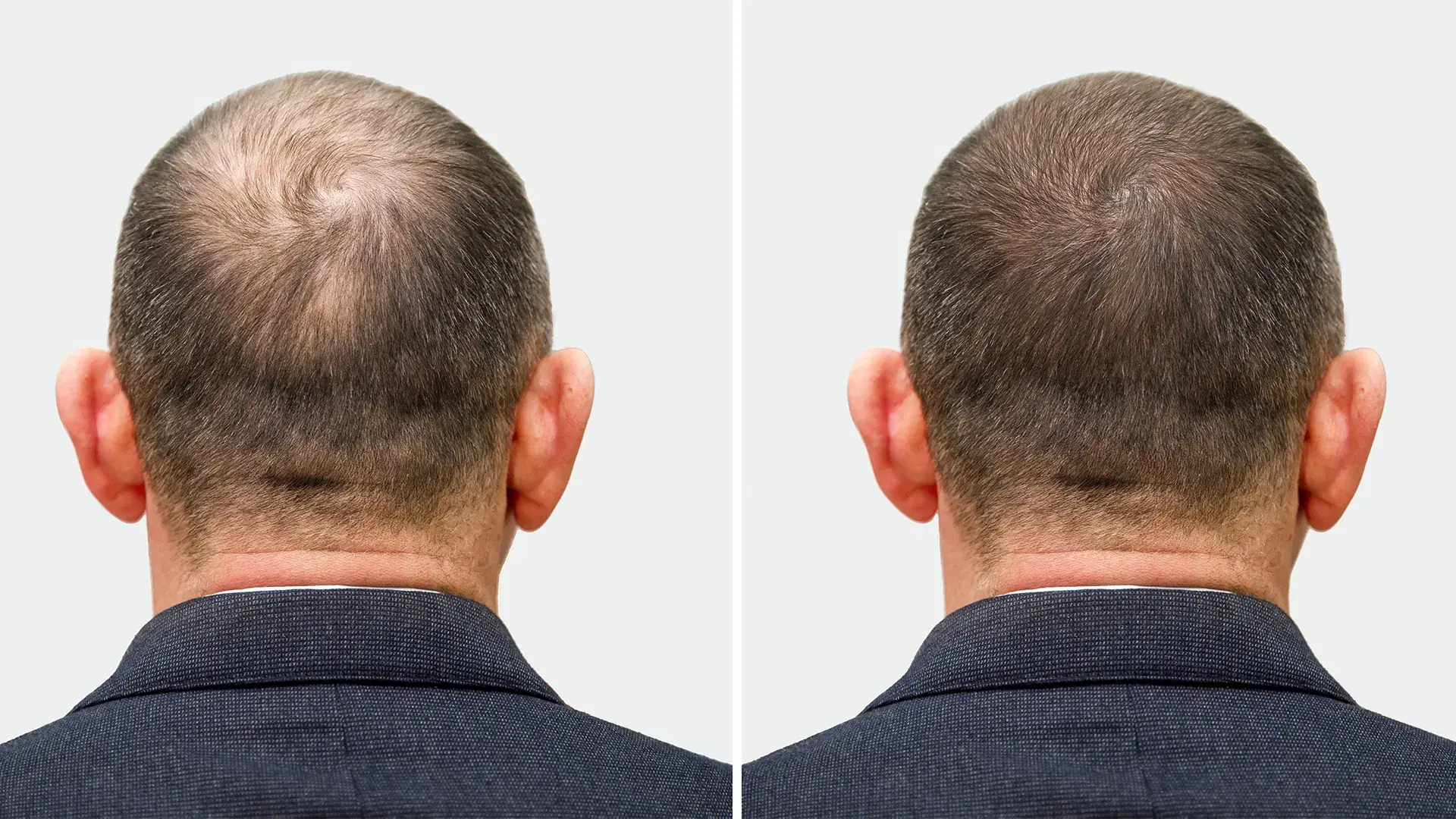
Conclusion
Hair growth is a complex but manageable process. When follicles are supported with proper nutrition, scalp care, and the right treatments, hair can grow stronger and healthier over time.
Understanding how hair grows, what slows it down, and which solutions truly work allows you to make informed decisions. Whether you choose natural methods, medical therapies, or advanced treatments, consistency and care are the real keys to long-term hair health.